As a startup owner, jumping in and of the trickiness of taxes is crucial for the financial health and compliance of your business, especially in 2024!
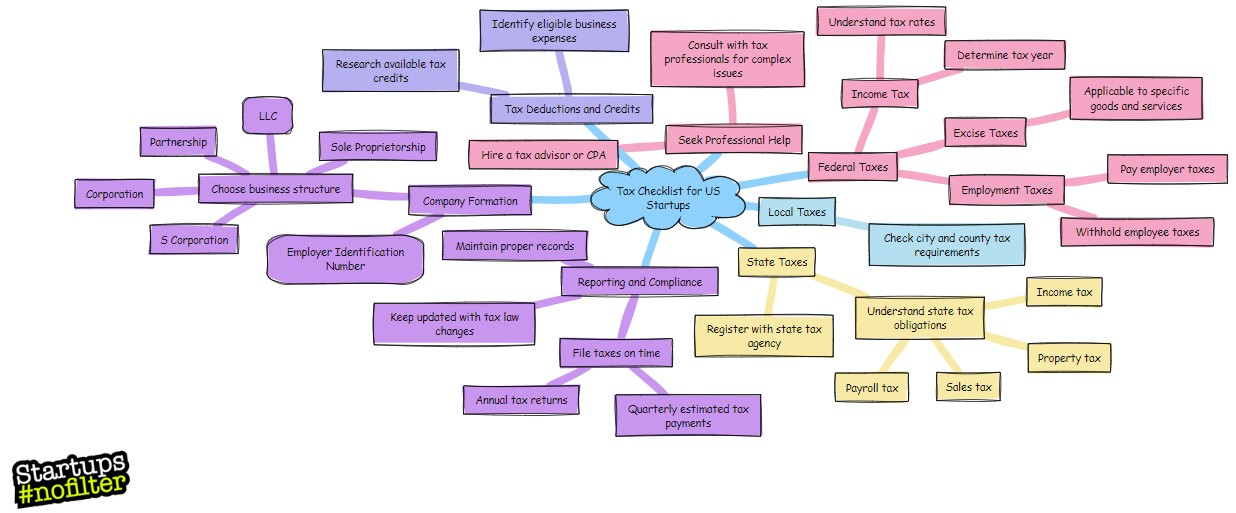
Here we give you a list of topics related to taxes for startups, designed to help you understand and manage your startup company tax obligations effectively:
15 Item Tax Checklist for Startup Owners:
- Tax Classification: You’ll need to understand the different tax classifications available for startups, such as sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation, or limited liability company (LLC), and how each impacts your tax responsibilities.
- Tax Obligations: It’s essential to be aware of the various federal, state, and local tax obligations your startup may have, including income tax, employment tax, sales tax, and property tax.
- Tax Incentives and Credits: Explore potential tax incentives and credits that could benefit your startup, such as research and development (R&D) tax credits or small business tax credits.
- Tax Deductions: Learn about the tax deductions you can claim for your startup, including deductions for business expenses, startup costs, and asset depreciation.
- Employee Taxes: Understand the tax implications of hiring employees, including payroll taxes, withholding taxes, and taxation of employee benefits.
- Equity Compensation: Familiarize yourself with the tax treatment of equity compensation options for your employees, such as stock options, restricted stock units (RSUs), or employee stock purchase plans (ESPPs).
- State and Local Taxes: Consider state-specific tax obligations for your startup, such as state income tax, franchise tax, and local business taxes – these can get very costly!
- International Taxation: If your startup operates internationally, be aware of the tax implications, including foreign income tax, value-added tax (VAT), and tax treaties.
- Tax Planning Strategies: Implement tax planning strategies to minimize your startup’s tax liabilities, such as choosing the right legal structure and timing income and expenses effectively. A classic strategy is finding the right tax haven country to save some tax money.
- Tax Compliance: Ensure your startup complies with tax laws and regulations by filing tax returns accurately, maintaining financial records, and responding to tax audits if necessary.
- Tax Reform: Stay informed about changes in tax laws and regulations that may affect your startup, such as recent tax reform legislation.
- Taxation of Funding Rounds: Understand the tax implications of different funding rounds for your startup, including seed funding, venture capital investment, or crowdfunding.
- Exit Strategies: Consider the tax consequences of potential exit strategies for your startup, such as mergers and acquisitions or initial public offerings (IPOs).
- Taxation of Intellectual Property: Be aware of the tax treatment of your startup’s intellectual property assets, such as patents, trademarks, and copyrights.
- Tax Reporting Software and Tools: Utilize tax reporting software and tools designed for startups to streamline your tax compliance processes and minimize errors.
By addressing these topics, you can proactively manage your startup’s tax affairs and ensure financial stability and compliance as you grow your business.
3 Tax Warnings for Every Small Business Startup Owner to Take Note of in 2024:
- Stay organized from day one: Keeping accurate records of all your income and expenses is crucial. Failure to maintain proper records can lead to errors in tax filings, which may result in penalties or audits. Invest in accounting software or hire a professional accountant to help you stay organized and ensure compliance with tax laws.
- Understand your tax obligations: As a small business owner, you need to be aware of various taxes you’re responsible for, including income tax, self-employment tax, sales tax (if applicable), and payroll taxes (if you have employees). Ignorance of your tax obligations can lead to costly mistakes. Consider consulting with a tax advisor or accountant to understand your specific tax liabilities and obligations.
- Plan for tax payments: Unlike employees who have taxes withheld from their paychecks, business owners are typically responsible for making estimated tax payments throughout the year. Failing to set aside funds for these payments can result in cash flow issues or unexpected tax bills come tax season. Make sure to budget for taxes and set aside a portion of your income regularly to cover your tax liabilities. It’s also essential to understand tax deadlines and avoid late payment penalties by filing and paying on time.
Additional:
- Tax Breaks for Startups: Tax Holidays, Tax Considerations, Tax Benefits and Tax Incentives for Startups – Startups can take advantage of various tax breaks such as the R&D tax credit, small business health care tax credit, startup tax credit, and retirement plan tax credit to reduce their tax burden and improve their financial position.
- Tax Filing for Startups in America – Startups must properly file their taxes, including quarterly estimated payments, deducting startup expenses, separating business and personal finances, and working with tax professionals to ensure compliance and maximize tax savings.
Looking for Startup Tax Havens? Here are a few Options:
Share this!

Editor of Startups #nofilter


