There is no universally agreed upon definition for how long a company retains its “startup” status, as it is a somewhat subjective term. However, here are some common perspectives on when a company typically loses its startup status:
- After being in operation for 5-10 years. Many experts consider a company to no longer be a startup after being in business for around 5-10 years.
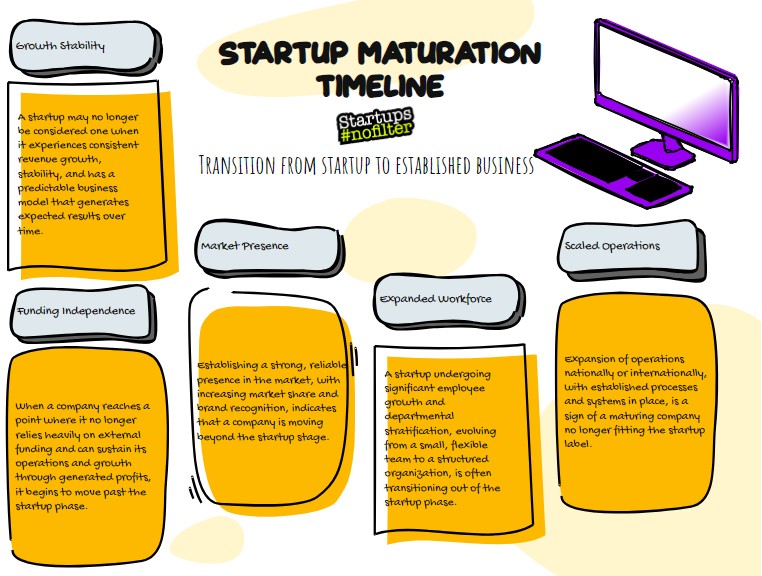
- After a successful exit event (IPO or acquisition). Once a startup goes public via an IPO or gets acquired by another company, it is generally no longer considered a startup.
- After reaching a certain revenue threshold or size. Some define the end of the startup phase as when a company exceeds $20-100 million in annual revenue or grows to have hundreds of employees.
- After establishing their product-market fit. Once a startup finds a repeatable, scalable business model and market position, some say it has outgrown the startup phase.
- After shifting from a startup to growth-stage company mentality and processes. The mindset and agility of a startup evolves as it matures.
- Crunchbase says that it occurs after a company moves past its break-even point money-wise and that is generating revenue — which means it’s growing naturally and organically — is no longer a startup.
So in summary, while there is no definitive rule, losing startup status typically happens somewhere between 5-10 years of operation, a major exit event, reaching significant revenue/employee scale, or evolving beyond the startup mentality and model. But it remains a subjective distinction.
You may be wondering something far more interesting than the topic of when does a startup lose its status as a startup. It is quite subjective to speculate as to when a startup is no longer considered a startup. But how about this: what is the statistic related to how many startups move past the startup stage?
Or put another way – how many startups will succeed, so that they can be classified as a proper hi-tech or functioning, profitable company?
The answer to how many startups actually move past the status of startup phase is only 10%. Which means that 90% of startups will fail!
And beyond that, only around 40% of startups are profitable, while others put the number lower, around 25-30% reaching profitability. Which means slightly more startups can claim they moved past the phase of being able to call themselves startups.

Editor of Startups #nofilter


